
|

| 产地 | 进口、国产 |
| 品牌 | 上海莼试 |
| 保存条件 | Store at -20 °C |
| 货号 | CS12371 |
| 应用范围 | ELISA=1:500-1000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 IF=1:50-200 |
| CAS编号 | |
| 抗体名 | Anti-Nav1.5/SCN5A |
| 克隆性 | 是 |
| 靶点 | 详见说明书 |
| 适应物种 | 详见说明书 |
| 形态 | 详见说明书 |
| 宿主 | 详见说明书 |
| 亚型 | IgG |
| 标识物 | 详见说明书 |
| 浓度 | 1mg/1ml% |
| 免疫原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human Nav1.5/SCN5A |
产品订购信息:
英文名称 Anti-Nav1.5/SCN5A
中文名称 电压门控钠通道5α抗体品牌
别 名 Cardiac tetrodotoxin insensitive voltage dependent sodium channel alpha subunit; CDCD2; CMD1E; CMPD2; HB1; HB2; HBBD; HH1; ICCD; IVF; LQT3; PFHB1; Scn5a (gene name); Scn5a; SCN5A_HUMAN; Sodium channel protein cardiac muscle alpha subunit; Sodium channel protein cardiac muscle alpha-subunit; Sodium channel protein cardiac muscle subunit alpha; Sodium channel protein type 5 subunit alpha; Sodium channel protein type V alpha subunit; Sodium channel protein type V subunit alpha; SSS1; VF1; Voltage gated sodium channel alpha subunit Nav1.5; Voltage-gated sodium channel alpha subunit Nav1.5; Voltage-gated sodium channel subunit alpha Nav1.5.

浓 度 1mg/1ml
规 格 0.2ml/200μg
抗体来源 Rabbit
克隆类型 polyclonal
交叉反应 Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Dog, Pig, Horse, Rabbit, Zebrafish, Sheep, Chimpanzee, mpanzee
产品类型 一抗
研究领域
蛋白分子量 predicted molecular weight: 227kDa
性 状 Lyophilized or Liquid
免 疫 原 KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human Nav1.5/SCN5A
亚 型 IgG
纯化方法 affinity purified by Protein A
储 存 液 Preservative: 15mM Sodium Azide, Constituents: 1% BSA, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4
电压门控钠通道5α抗体品牌 产品应用 ELISA=1:500-1000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 IF=1:50-200
(石蜡切片需做抗原修复)
not yet tested in other applications.
optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
保存条件 Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C.
Important Note This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
产品介绍 This protein mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. It is a tetrodotoxin-resistant Na(+) channel isoform. This channel is responsible for the initial upstroke of the action potential.
Function : This protein mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. It is a tetrodotoxin-resistant Na(+) channel isoform. This channel is responsible for the initial upstroke of the action potential. Channel inactivation is regulated by intracellular calcium levels.
Subunit : Interacts with the PDZ domain of the syntrophin SNTA1, SNTB1 and SNTB2 (By similarity). Interacts with NEDD4, NEDD4L, WWP2 and GPD1L. Interacts with CALM. Interacts with FGF13; the interaction is direct and may regulate SNC5A density at membranes and function.
Subcellular Location : Membrane.
Tissue Specificity : Found in jejunal circular smooth muscle cells (at protein level). Expressed in human atrial and ventricular cardiac muscle but not in adult skeletal muscle, brain, myometrium, liver, or spleen. Isoform 4 is expressed in brain.
Post-translational modifications : Regulated through phosphorylation by CaMK2D (By similarity).
Ubiquitinated by NEDD4L; which promotes its endocytosis. Does not seem to be ubiquitinated by NEDD4 or WWP2.
DISEASE : Defects in SCN5A are a cause of progressive familial heart block type 1A (PFHB1A) [MIM:113900]; also known as Lenegre-Lev disease or progressive cardiac conduction defect (PCCD). PFHB1A is an autosomal dominant cardiac bundle branch disorder that may progress to complete heart block. PFHB1A is characterized by progressive alteration of cardiac conduction through the His-Purkinje system with right or left bundle branch block and widening of QRS complexes, leading to complete atrioventricular block and causing syncope and sudden death. [DISEASE] Defects in SCN5A are the cause of long QT syndrome type 3 (LQT3) [MIM:603830]. Long QT syndromes are heart disorders characterized by a prolonged QT interval on the ECG and polymorphic ventricular arrhythmias. They cause syncope and sudden death in response to exercise or emotional stress. LQT3 inheritance is an autosomal dominant.
Defects in SCN5A are the cause of Brugada syndrome type 1 (BRGDA1) [MIM:601144]. An autosomal dominant tachyarrhythmia characterized by right bundle branch block and ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It can cause the ventricles to beat so fast that the blood is prevented from circulating efficiently in the body. When this situation occurs (called ventricular fibrillation), the individual will faint and may die in a few minutes if the heart is not reset.
Defects in SCN5A are the cause of sick sinus syndrome type 1 (SSS1) [MIM:608567]. The term 'sick sinus syndrome' encompasses a variety of conditions caused by sinus node dysfunction. The most common clinical manifestations are syncope, presyncope, dizziness, and fatigue. Electrocardiogram typically shows sinus bradycardia, sinus arrest, and/or sinoatrial block. Episodes of atrial tachycardias coexisting with sinus bradycardia ('tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome') are also common in this disorder. SSS occurs most often in the elderly associated with underlying heart disease or previous cardiac surgery, but can also occur in the fetus, infant, or child without heart disease or other contributing factors, in which case it is considered to be a congenital disorder.
Defects in SCN5A are the cause of familial paroxysmal ventricular fibrillation type 1 (VF1) [MIM:603829]. A cardiac arrhythmia marked by fibrillary contractions of the ventricular muscle due to rapid repetitive excitation of myocardial fibers without coordinated contraction of the ventricle and by absence of atrial activity.
Defects in SCN5A may be a cause of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) [MIM:272120]. SIDS is the sudden death of an infant younger than 1 year that remains unexplained after a thorough case investigation, including performance of a complete autopsy, examination of the death scene, and review of clinical history. Pathophysiologic mechanisms for SIDS may include respiratory dysfunction, cardiac dysrhythmias, cardiorespiratory instability, and inborn errors of metabolism, but definitive pathogenic mechanisms precipitating an infant sudden death remain elusive. Long QT syndromes-associated mutations can be responsible for some of SIDS cases.
Defects in SCN5A may be a cause of familial atrial standstill (FAS) [MIM:108770]. Atrial standstill is an extremely rare arrhythmia, characterized by the absence of electrical and mechanical activity in the atria. Electrocardiographically, it is characterized by bradycardia, the absence of P waves, and a junctional narrow complex escape rhythm.
Defects in SCN5A are the cause of cardiomyopathy dilated type 1E (CMD1E) [MIM:601154]; also known as dilated cardiomyopathy with conduction disorder and arrhythmia or dilated cardiomyopathy with conduction defect 2. Dilated cardiomyopathy is a disorder characterized by ventricular dilation and impaired systolic function, resulting in congestive heart failure and arrhythmia. Patients are at risk of premature death.
Defects in SCN5A are the cause of familial atrial fibrillation type 10 (ATFB10) [MIM:614022]. ATFB10 is a familial form of atrial fibrillation, a common sustained cardiac rhythm disturbance. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by disorganized atrial electrical activity and ineffective atrial contraction promoting blood stasis in the atria and reduces ventricular filling. It can result in palpitations, syncope, thromboembolic stroke, and congestive heart failure.
Similarity : Belongs to the sodium channel (TC 1.A.1.10) family. Nav1.5/SCN5A subfamily.
Contains 1 IQ domain.
Database links : UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot: Q14524.2
Involvement in disease;Defects in SCN5A are a cause of progressive familial heart block type 1A (PFHB1A); also known as Lenegre-Lev disease or progressive cardiac conduction defect (PCCD). PFHB1A is an autosomal dominant cardiac bundle branch disorder that may progress to complete heart block. PFHB1A is characterized by progressive alteration of cardiac conduction through the His-Purkinje system with right or left bundle branch block and widening of QRS complexes, leading to complete atrio-ventricular block and causing syncope and sudden death.
Defects in SCN5A are the cause of long QT syndrome type 3 (LQT3). Long QT syndromes are heart disorders characterized by a prolonged QT interval on the ECG and polymorphic ventricular arrhythmias. They cause syncope and sudden death in response to exercise or emotional stress. LQT3 inheritance is an autosomal dominant.
Defects in SCN5A are the cause of Brugada syndrome type 1 (BRS1). BRS1 is an autosomal dominant tachyarrhythmia characterized by right bundle branch block and ST segment elevation on an electrocardiogram (ECG). It can cause the ventricles to beat so fast that the blood is prevented from circulating efficiently in the body. When this situation occurs (called ventricular fibrillation), the individual will faint and may die in a few minutes if the heart is not reset.

改良麦康凯肉汤冻干配套试剂SR0240支添加于(025(025
Peptone 140 (Soytone) 蛋白胨-140 100g incubation media Peptone 140 (Soytone) 蛋白胨-140 100g
小肠耶尔森氏菌 酒精酵母 支/瓶
大肠杆菌显色培养基l用于快速、准确检测大肠杆菌,培养24小时,显蓝绿色
MiddleBrook7H10琼脂 250g 用于分枝杆菌的分离培养
改良沙氏琼脂培养基250g用于真菌培养
LB琼脂 250(g) incubation media LB琼脂 250(g)
NZM肉汤 NZM Broth 100克 BR
KF链球菌琼脂于链球菌的选择性分离及计数(SN标准)incubationmediaKF链球菌琼脂于链球菌的选择性分离及计数(SN标准)
霍乱红胨水 20支 霍乱弧菌的霍乱红试验
月桂基盐胰蛋白胨肉汤(LST)2220g用于多管发酵法测定大肠菌群和粪大肠菌GB4789.3-20/T4789.38-2008,GB/T4789.39-200...
MRVP 培养基 (Clarks and Lubs 培养基) (CM0043) Oxoid incubation media MRVP 培养基 (Clarks and Lubs 培养基) (CM0043) Oxoid
耐久肠球菌(坚韧链球菌) 支/瓶
SD-39Agar
MycoplasmaSemi-fluidMedium
CL-0164NAMALWA(人Butt's细胞)5×106cells/瓶×2
CD84 Others Cynomolgus 食蟹猴 CD84 人细胞裂解液 (阳性对照)
人成纤维细胞-心室裂解物HCF-av L
CCD-1095Sk细胞,人浸润性导管癌旁皮肤细胞 鼠细胞,H22-H8D8细胞 脑成纤维细胞Many types of cells包装:5 × 105次方(1ml)
BC3H1(小鼠细胞) 5×106cells/瓶×2
HUASMC Pellet 人脐动脉平滑肌细胞团块 > 1 mio.cells 人上皮细胞裂解物HPEpiCL
电压门控钠通道5α抗体品牌CL-0162MS1(小鼠胰岛内皮细胞)5×106cells/瓶×2
F7 Others Mouse 小鼠 Coagulation Factor VII / FVII / F7 CHO细胞裂解液 (阳性对照)
人心肌细胞-裂解物HCM-a L
家猪皮肤细胞;SSC-S1 癌细胞,ZR-75-1细胞 NS1细胞,小鼠细胞
腺病毒转化的人胚肾细胞;AAV-293
HA Others H5N1 甲型 H5N1 (A/chicken/Egypt/2253-1/2006) 血凝素HA1 (Hemagglutinin) 人细胞裂解液 (阳性对照)

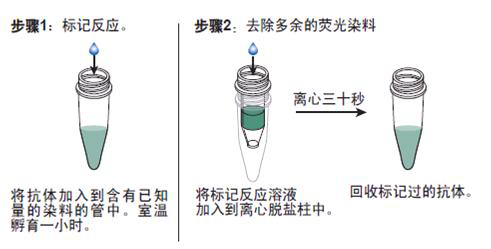
抗体的生物素化标记实验要点:
1. 电压门控钠通道5α抗体品牌 如在反应混合液中有叠氮钠或游离氨基存在,会抑制标记反应。因此,蛋白质在反应前要对 0.1mol/L碳酸氢钠缓冲液或0.5mol/L硼酸缓冲液充分透析;
2.所用的NHSB及待生物素化蛋白质之间的分子比按蛋白质表面的ε-氨基的密度会有所不同,选择不当则影响标记的效率,应先用几个不同的分子比来筛选最适条件;
3.用NHSB量过量也是不利的,抗原的结合位点可能因此被封闭,导致抗体失活;
4.由于抗体的氨基不易接近可能造成生物素化不足,此时可加入去污剂如 Triton x-100, Tween20等;
5.当游离ε-氨基(赖氨酸残基的氨基)存在于抗体的抗原结合位点时,或位于酶的催化位点时,生物素化会降低或损伤抗体蛋白的结合力或活性;
6.生物素还可能与不同的功能基团,如羰基、氨基、巯基、异咪唑基及苯酚基,也可与糖基共价结合;
7.交联反应后,应充分透析,否则,残余的生物素会对生物素化抗体与亲和素的结合产生竞争作用;
8.在细胞的荧光标记实验中,中和亲和素的本底低,但由于链霉亲和素含有少量正电荷,故对某些细胞可导致高本底。
抗体的鉴定:
1)电压门控钠通道5α抗体品牌 抗体的效价鉴定:不管是用于诊断还是用于,制备抗体的目的都是要求较高效价。不同的抗原制备的抗体,要求的效价不一。鉴定效价的方法很多,包括有试管凝集反应,琼脂扩散试验,酶联免疫吸附试验等。常用的抗原所制备的抗体一般都有约成的鉴定效价的方法,以资比较。如制备抗抗体的效价,一般就采用琼脂扩散试验来鉴定。
2)抗体的特异性鉴定:抗体的特异性是指与相应抗原或近似抗原物质的识别能力。抗体的特异性高,它的识别能力就强。衡量特异性通常以交叉反应率来表示。交叉反应率可用竞争抑制试验测定。以不同浓度抗原和近似抗原分别做竞争抑制曲线,计算各自的结合率,求出各自在IC50时的浓度,并按公式计算交叉反应率。
如果所用抗原浓度IC50浓度为pg/管,而一些近似抗原物质的IC50浓度几乎是无穷大时,表示这一抗血清与其他抗原物质的交叉反应率近似为0,即该血清的特异性较好。
3)抗体亲和力:是指抗体和抗原结合的牢固程度。亲和力的高低是由抗原分子的大小,抗体分子的结合位点与抗原决定簇之间立体构型的合适度决定的。有助于维持抗原抗体复合物稳定的分子间力有氢键,疏水键,侧链相反电荷基因的库仑力,范德华力和空间斥力。亲和力常以亲和常数K表示,K的单位是L/mol。抗体亲和力的测定对抗体的筛选,确定抗体的用途,验证抗体的均一性等均有重要意义。